Publications
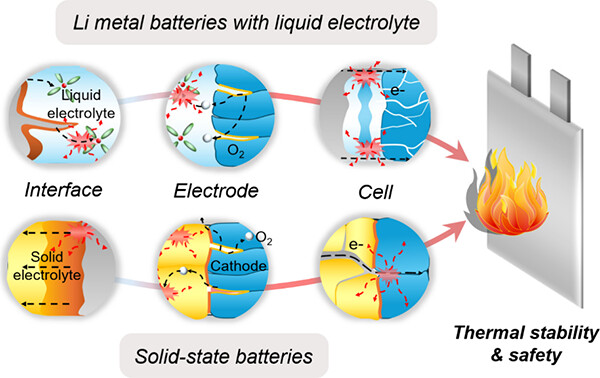
15. Mechanistic Understanding of Thermal Stability and Safety in Lithium Metal Batteries
Kausthubharam, B.S. Vishnugopi, A. S. J. Alujjage, V. Premnath, W.S. Tang, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper Chemical Reviews (2025)
Abstract
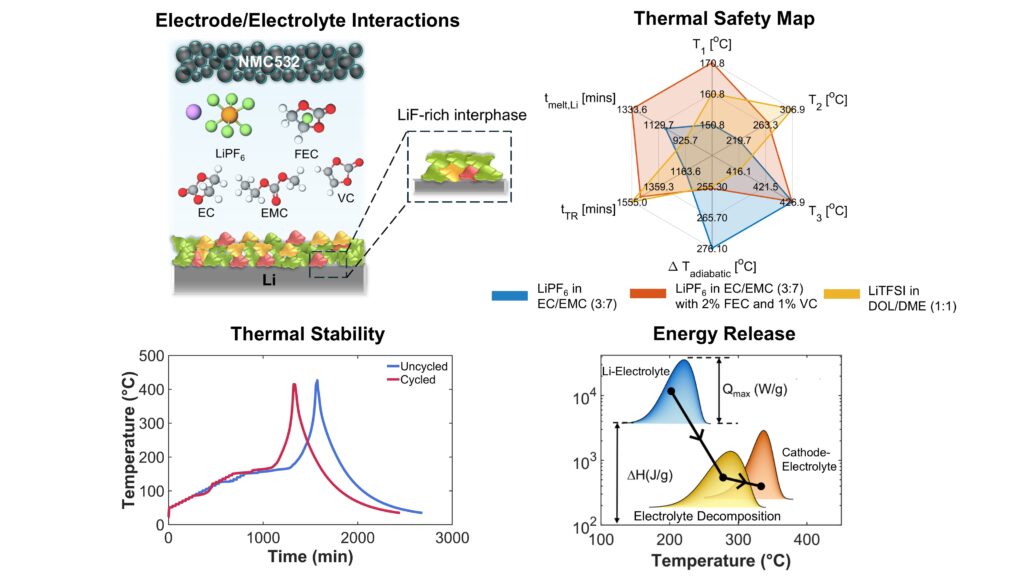
14. Interrogating the Thermo-Electrochemical Instability and Safety in Lithium Metal Electrodes with Liquid Electrolytes
R. Saha, A. S. J. Alujjage, B.S. Vishnugopi, A. Karmakar, D. R. R. Kannan, D. Tewari, F. Gray, V. Premnath, W.S. Tang, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper Advanced Energy Materials, 202504145 (2025)
Abstract
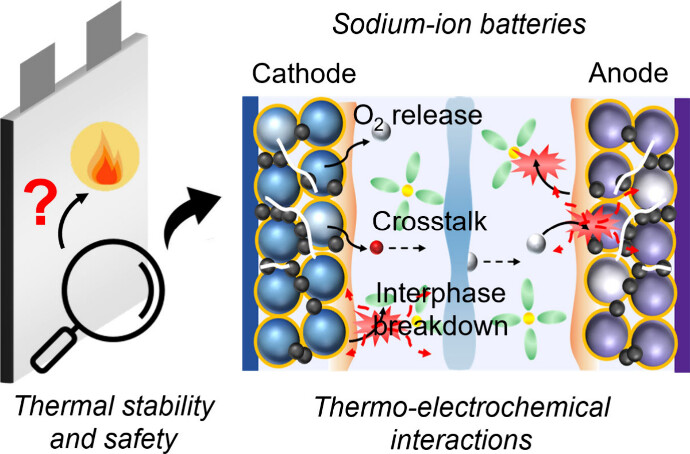
13. Perspective on Thermal Stability and Safety of Sodium-Ion Batteries [Editor's Choice]
Kausthubharam, B.S. Vishnugopi, A. Sengupta, D.R.R. Kannan, V. Premnath, W.S. Tang, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper ACS Energy Letters, 10, 5383 (2025)
Abstract
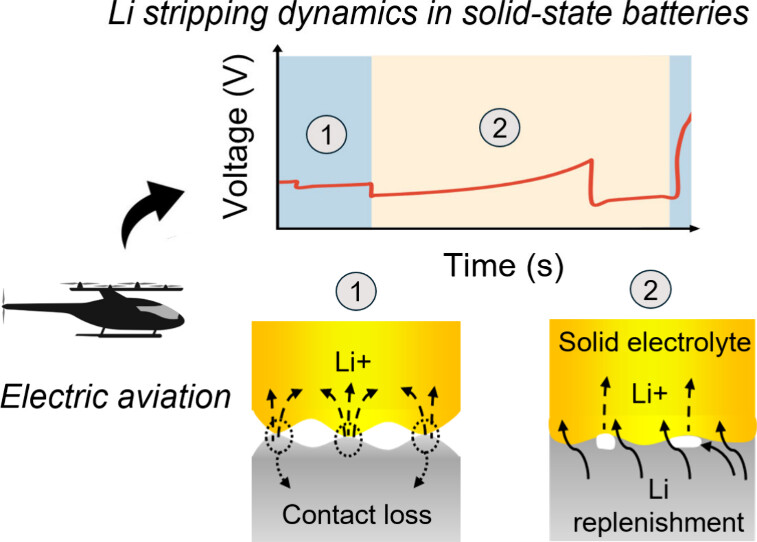
12. Mechanistic Interrogation of Li Stripping under Dynamic Operation in Solid-State Batteries
Kausthubharam, A. Ayyaswamy, B.S. Vishnugopi, D. Tewari, D.R.R. Kannan, V. Premnath, W.S. Tang, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper ACS Energy Letters, 10, 4212 (2025)
Abstract
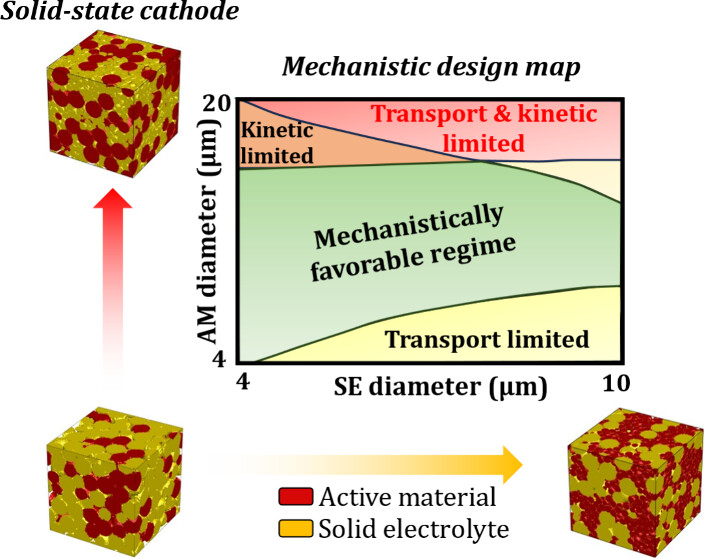
11. Co-design of Active Material and Solid Electrolyte Particulate Phases in Solid-State Battery Composite Electrodes
A. K. Sharma, B.S. Vishnugopi , A. Ayyaswamy, A. Nath, D. Chatterjee, D. Tewari, M. S. Ng, W. S. Tang, V. Premnath, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2025)
Abstract
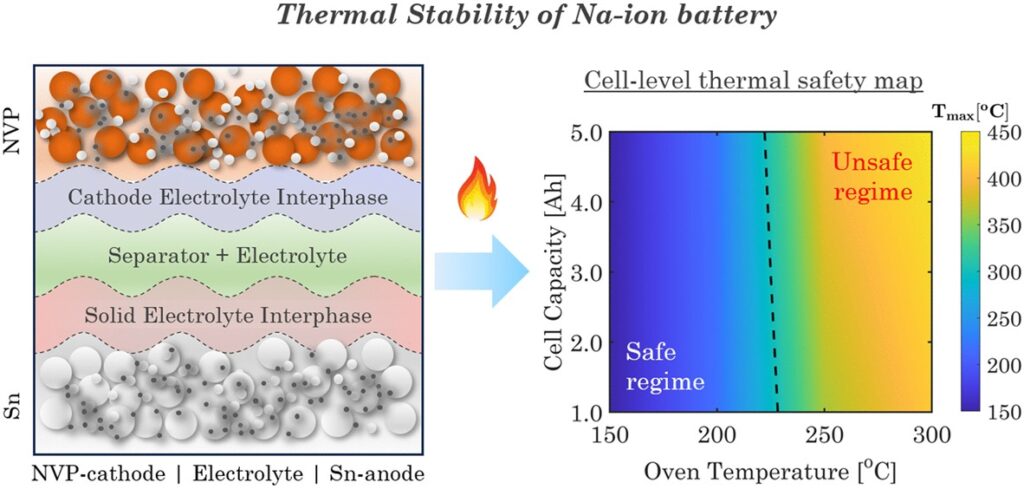
10. Electrode–Electrolyte Interactions Dictate Thermal Stability of Sodium-Ion Batteries
S. Sarkar, A. Karmakar, B.S. Vishnugopi , J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper Chemical Communications, 60, 12868 (2025)
Abstract
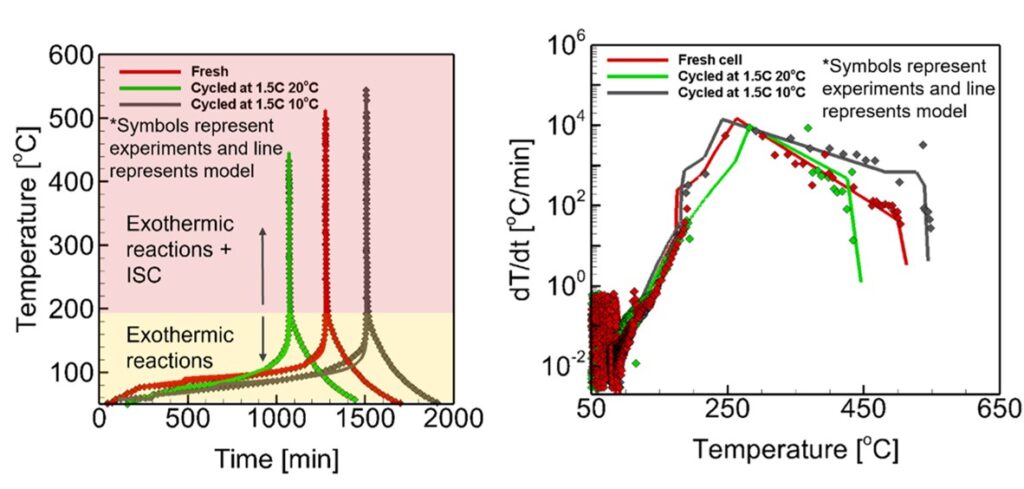
9. Quantifying the effect of degradation modes on Li-ion battery thermal instability and safety
V. Kabra, A. Karmakar, B.S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper Energy Storage Materials, 74, 103878 (2024)
Abstract
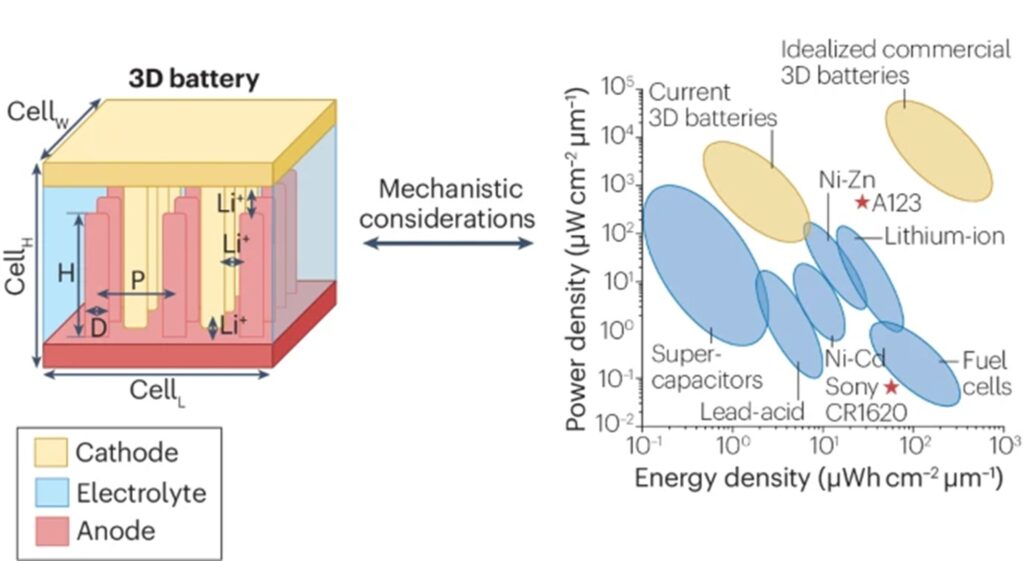
8. Performance Metrics and Mechanistic Considerations for the Development of 3D Batteries
K. Nieto, D.S. Windsor, B.S. Vishnugopi , P. P. Mukherjee and A.L. Prieto
Journal Paper Nature Reviews Chemistry, 9, 118 (2025)
Abstract
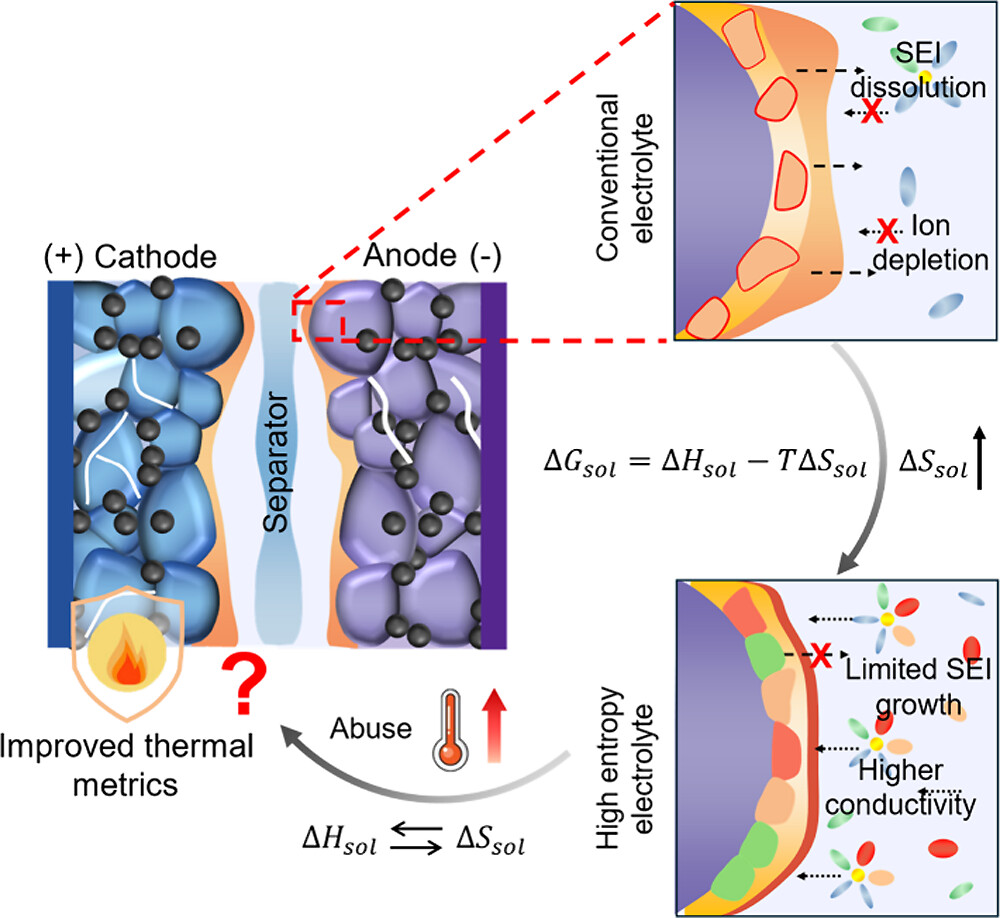
7. High-Entropy Electrolytes in Sodium-Ion Batteries: Performance and Safety Perspective
S. Sudhakaran, Kausthubharam, B.S. Vishnugopi, P. P. Mukherjee, and V. G. Pol
Journal Paper ACS Energy Letters, 10, 4567 (2025)
Abstract
6. MoChA: Modeling, Characterization and Analytics in Electrochemical Energy Systems
D. Chatterjee, P. Mitra, A. Singla, S. Banerjee, A. S. J. Alujjage and P. P. Mukherjee
Journal Paper ACS Energy Letters, 10, 3430 (2025)
Abstract
5. Synergistic Influence of Anode Composition and Electrolyte Interactions in Sodium-Ion Cells
P. Ranganathan , B.S. Vishnugopi, F. S. Gray, D. R. R. Kannan, A. Karmakar, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
In Preparation (2025)
4. Impact of Electrolyte Volume on Lithium Plating Dynamics and Thermal Stability in Lithium-Ion Batteries
A. S. J. Alujjage, S. P. Rangrajan, A. Ayyaswamy, A. Karmakar, B.S. Vishnugopi, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
In Preparation (2025)
3. Mechanistic Insight into the Thermal Stability of Solid-State Batteries
B.S. Vishnugopi, Kaustubharam, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
In Preparation (2025)
2. Fundamental Understanding of the Thermal Stability and Safety of Next-Generation Lithium Metal Batteries
Kausthubharam, A.S.J. Alujjage, B.S. Vishnugopi, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
In Preparation (2025)
1. Degradation-Safety Interactions in Na-Ion Batteries
Kausthubharam, A. Sengupta, B.S. Vishnugopi, J.A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
In Preparation (2025)
Conference Presentations
22. Mechanistic Role of Electrode/Electrolyte Interactions on the Thermal Stability of Sodium-Ion Batteries
P. Ranganathan, A. Karmakar, A. Sengupta, B. S. Vishnugopi, G. Frederick, D. R. R. Kannan, V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
21. Pressure-Driven Thermo-Electrochemical Interaction and Safety in Solid-State Batteries
A. K. Sharma, B. S. Vishnugopi, A. Miguel, D. Tewari V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
20. Stripping Behavior of Solid-State Batteries Under Dynamic Discharge Loads for Electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
Kausthubharam, B. S. Vishnugopi, D. R. R. Kanan, G. Frederick, V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
19. Investigating Thermo-Electrochemical Stability of Lithium Metal Electrodes with Liquid Electrolytes
R. Saha, A. S. J. Alujjage, A. Karmakar, B. S. Vishnugopi, D. R. R. Kanan, G. Frederick, V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
18. Co-Design of Particle Size and External Pressure in All-Solid-State Battery Cathodes
M. A. Nafi, B. S. Vishnugopi, D. R. R. Kanan, G. Frederick, V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
17. Role of Cathode-Electrolyte Interphase in Thermal Stability of High-Energy Na-Ion Batteries
A. Sengputa, B. S. Vishnugopi, D. R. R. Kanan, G. Frederick, V. Premnath, W. S. Tang, J. A. Jeevarajan and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 248th ECS Meeting, Chicago, IL (2025)
16. Mechanistic Insights into Interface Instability of Sodium Metal Electrodes
P. P. Mukherjee, A. Singla and B. S. Vishnugopi
Conference Presentation MRS Spring Meeting & Exhibit, Seattle, WA (2025)
18. Mechanistic Interactions at Scale in Electrochemical Energy Storage
P. P. Mukherjee
Departmental Seminar Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin–Madison (2025)
15. Gradients and Instabilities in Solid-State Battery Architectures (invited)
P. P. Mukherjee, B. S. Vishnugopi, A. Ayyaswamy
Conference Presentation PRiME 2024, Honolulu, HI (2024)
14. Interface Dynamics and Heterogeneities in Solid-State Batteries
B. S. Vishnugopi, K. G. Naik and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation PRiME 2024, Honolulu, HI (2024)
13.Thermo-Electrochemical Stability of Solid-State Batteries (invited)
P. P. Mukherjee and B. S. Vishnugopi
Conference Presentation 245th ECS Meeting, San Francisco, CA (2024)
12. External Cooling and Degradation Interplay in Lithium-Ion Battery Fast Charging
A. Karmakar, B. S. Vishnugopi, and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 245th ECS Meeting, San Francisco, CA (2024)
11. Interrogating Internal Temperature Evolution in Li-Ion Cells
A. S. J. Alujjage, B. S. Vishnugopi, Y. Barsukov, D. P. Magee and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 245th ECS Meeting, San Francisco, CA (2024)
10. Mechanistic Analysis of Interface Instability in Solid-State Batteries (invited)
B. S. Vishnugopi, K. G. Naik and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation TMS Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Orlando, FL (2024)
9. Mechanistic Interactions at Scale in Electrochemical Energy Storage
P. P. Mukherjee
Departmental Seminar Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, IL (2024)
9. Operando Monitoring and Analytics of Internal Temperature Dynamics in Li-Ion Batteries
A. S. J. Alujjage, B. S. Vishnugopi, Y. Barsukov, D. P. Magee and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation NSF Student Poster Competition, Portland, OR (2024)
8. Mechanistic Interrogation of Alloy Interlayers in Solid-State Batteries
D. Chatterjee, K. G. Naik, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 2024 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston, MA (2024)
7. Mechanistic Analysis of Solid Electrolyte Interphase Interactions in Sodium Metal Electrodes
A. Singla, K. G. Naik, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 2024 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston, MA (2024)
6. Synergistic Influence of Anode Composition and Electrolyte Interactions in Sodium-Ion Cells
P. Ranganathan, S. Sarkar, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 2024 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston, MA (2024)
5. Mechanistic Role of External Stack Pressure on the Thermal Stability of Solid-State Batteries
M. T. Hasan, A. Karmakar, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 2024 MRS Fall Meeting & Exhibit, Boston, MA (2024)
4. Thermo-Electrochemical Interactions in Solid-State Batteries (invited)
P. P. Mukherjee and B. S. Vishnugopi
Conference Presentation 244th ECS Meeting, Gothenburg, Sweden (2023)
3. Void Growth Dynamics in Solid-State Batteries
B. S. Vishnugopi, K. G. Naik and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 244th ECS Meeting, Gothenburg, Sweden (2023)
2. Mechanistic Underpinnings of Heterogeneities in Solid-State Battery Cathode
K. G. Naik, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 244th ECS Meeting, Gothenburg, Sweden (2023)
1. Mechanics-Coupled Interface Kinetics in Solid-State Batteries
D. Chatterjee, K. G. Naik, B. S. Vishnugopi and P. P. Mukherjee
Conference Presentation 244th ECS Meeting, Gothenburg, Sweden (2023)


